Table of Contents
- Understanding Is Gynecomastia Surgery Painful?
- What Is Gynecomastia?
- Symptoms Of Gynecomastia
- Causes Of Gynecomastia
- Diagnosis And Assessment of Gynecomastia
- Types of Gynecomastia Surgery
- Risks And Complications of Gynecomastia Surgery
- Preparation For Gynecomastia Surgery
- Recovery Process For Gynecomastia Surgery
- Post-Operative Gynecomastia Surgery Care
- Benefits of Gynecomastia Surgery
- Gynecomastia Surgery Conclusion
Understanding Is Gynecomastia Surgery Painful?
Before we answer your question – is gynecomastia painful? A quick definition. Gynecomastia is a condition that affects men of all ages, causing enlarged breast tissue because of hormonal imbalances. Although it can be uncomfortable for those affected, treatments are available to reduce or eliminate the symptoms. One such treatment is surgery, which requires an in-depth knowledge of the procedure and its associated risks.
An important question often asked by potential patients is, ‘Is gynecomastia surgery painful?’ In this article, we will explore the pain associated with gynecomastia surgery, highlighting both the short- and long-term effects experienced by those who have undergone the operation. We will also discuss ways to minimize any discomfort before undergoing the procedure.
The physical and mental distress caused by gynecomastia can cause profound emotional turmoil for some sufferers. Surgery may seem drastic, but for many men, it provides much-needed relief from their condition. The prospect of surgery, however, can be daunting as people naturally fear what they don’t understand – especially when facing something potentially painful.
Understanding how painful it might be should be part of your decision-making when considering whether to undergo gynecomastia surgery. Knowing you’re prepared and informed on what to expect can help ease any anxieties surrounding the procedure itself, so let’s take a closer look at what you need to know about pain during gynecomastia surgery.
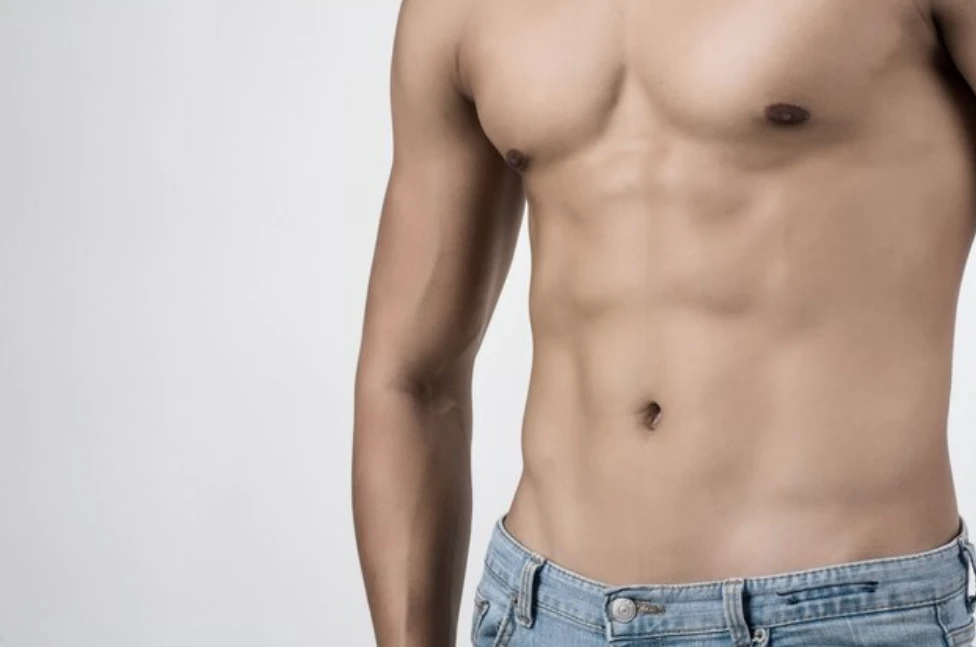

What Is Gynecomastia?
Gynecomastia is a medical condition in which male breast tissue enlarges disproportionately. It can affect one or both breasts and most commonly affects adolescent boys as they go through puberty. Sometimes, adult men may also experience gynecomastia because of hormonal changes or certain medications. The amount of breast tissue that develops varies from person to person, but it is usually not painful. However, if the breast tissue becomes large enough, it can cause physical discomfort and embarrassment for those affected. Treatment options include medication, lifestyle modifications such as weight loss, and gynecomastia surgery.
Symptoms Of Gynecomastia
Gynecomastia is a condition that affects many men, and it cannot be easy to deal with. Sometimes, the breasts may become tender or feel lumpy. Other symptoms include swollen nipples with discharge from them, discomfort in the area around the nipple, and darkening of the skin on the nipple.
Diagnosis for gynecomastia often involves a physical examination by a medical professional and blood tests to rule out other causes, such as hormone imbalances or liver disease. They may need further testing for any signs of underlying conditions like cancer. Treatment options depend on the severity of the case but typically involve lifestyle changes, such as diet and exercise, as well as medications or surgery if necessary. Surgery usually involves the removal of excess tissue using liposuction or mastectomy techniques while preserving normal tissue where possible.
Causes Of Gynecomastia
They divided the causes of gynecomastia into two categories: physiological and pathological. Physiological causes include hormone imbalances because of puberty, aging, and certain medical conditions such as liver and kidney disease. Drugs, alcohol use, and illicit substances such as anabolic steroids may cause pathological causes.
Patients must understand that there is no single cause for this condition; multiple factors can contribute to developing gynecomastia. Sometimes, it may even occur with no identifiable triggers. To determine gynecomastia caused if a patient’s symptoms, a doctor will perform a physical examination and review their medical history. We recommend diagnostic tests to identify potential underlying issues that could contribute to the condition. Depending on individual circumstances, these tests typically involve blood work, imaging studies, or biopsies.
With proper diagnosis and treatment, most patients affected by gynecomastia can achieve satisfactory results from their treatment plan. If the test results show it, we could also recommend hormone therapy to restore the body’s equilibrium. It is essential for individuals suffering from gynecomastia to seek professional advice to receive an accurate diagnosis and get medical care tailored to them.
Diagnosis And Assessment of Gynecomastia
Diagnosis and assessment of gynecomastia typically begin with a thorough physical exam, which may include an examination of the patient’s breasts. We can also perform blood tests to evaluate hormones such as testosterone, prolactin, and estradiol. An ultrasound or mammogram may be recommended if there is a suspicion of breast cancer. We may further evaluate using other imaging techniques, such as MRI.
Sometimes, additional testing, including biopsy and genetic testing, may be necessary to identify any underlying causes of gynecomastia. Treatment options will depend on an individual’s medical history and the severity of their condition. Patients must discuss all potential risks associated with surgery before deciding whether it is the right option.
Types of Gynecomastia Surgery
Gynecomastia surgery is highly specialized and can be performed in various ways. Each type of surgery carries risks and potential side effects, so it’s important to understand the nuances before undergoing treatment.
The most common gynecomastia surgery involves liposuction and direct glandular tissue excision. Liposuction involves suctioning excess fat from the chest periphery through small cannula incisions. This technique requires minimal downtime and allows fast recovery with no visible scarring after completed healing. Direct tissue excision involves removing glandular breast tissue that has grown because of hormonal changes or weight gain. While this method offers more dramatic results, it also comes with a longer recovery time and may leave some scarring because of the length of the infra-areolar incision required.
No matter which type of gynecomastia surgery you choose, discussing your concerns and expectations with your surgeon before beginning any treatment plan is essential. It’s imperative to ask questions “Is gynecomastia surgery painful?” regarding pain management strategies, anesthesia options, post-operative care instructions, and any other information that will help ensure your experience is as comfortable as possible.
Risks And Complications of Gynecomastia Surgery
Gynecomastia surgery is safe, but there are risks and potential complications associated with any surgery. Common side effects include pain, swelling, numbness or tingling in the chest area, bruising, and infection. Infrequently, residual contour irregularities or asymmetry may persist, especially if there is asymmetry preoperatively. Scarring can be an issue for some patients because of surgical incisions made during the procedure.
It is important to speak with your doctor about all potential risks before undergoing gynecomastia surgery so that you can make an informed decision regarding whether this procedure is right for you. Your doctor will also provide instructions on how best to care for yourself after the procedure to minimize the risk of complications arising from the surgery.
Preparation For Gynecomastia Surgery
The patient should adequately prepare for gynecomastia surgery. The doctor will provide instructions to ensure safe and successful outcomes. Sometimes, further tests, such as an electrocardiogram (ECG) or chest x-ray, may be required to rule out any underlying medical conditions like heart problems that could complicate the procedure. Patients need to inform their doctor of any medications they are taking before surgery, including supplements and herbal remedies, as these may need to be stopped temporarily before the operation.
In addition, the patient mustn’t smoke for at least two weeks before and after surgery, as this can increase the risk of complications during recovery. The patient should reduce or avoid alcohol intake to reduce anesthesia risks. Patients must follow all their doctor’s preoperative instructions to achieve optimal results from the procedure.
Recovery Process For Gynecomastia Surgery
Gynecomastia surgery’s recovery process is relatively straightforward and comfortable. The pain levels reported by most patients are mild or non-existent. It’s important to note that some procedures require general anesthesia, so those individuals may experience more discomfort post-surgery than those who underwent a procedure requiring local anesthetic only.
Patients can typically resume normal activities within one week of surgery but should avoid strenuous exercise and heavy lifting. It’s recommended that you wear a compression garment provided by your doctor while healing from the procedure, as this will help reduce swelling and promote better results.
Post-Operative Gynecomastia Surgery Care
After the surgery, following your doctor’s post-surgery instructions is incredibly important. Although gynecomastia surgery is not too painful, and there may be only minor discomfort during recovery, patients should still take care of their incision site for speedy healing.
It’s crucial to keep the area clean and dry after the procedure. To prevent infection, ensure they regularly change the bandages to avoid prolonged contact with unclean materials. Avoiding excessive exercise or any activity that strains the chest muscles until fully healed is essential – this can prevent damage or slow recovery time significantly. Showering must be done with caution; use lukewarm water instead of excessively hot water and mild soap since strong chemicals could irritate the wound further. Patients should wear loose clothing to place no pressure on the surgical site while it heals.
Pain medications can help ease any lingering aches caused by the surgery; Contact them if you have questions like “Is gynecomastia surgery painful?” and pain management during the post-surgery care period. Ultimately, following all the advice provided by medical professionals and taking good care of yourself will help you recover quickly and smoothly!
Benefits of Gynecomastia Surgery
Gynecomastia surgery is not painful, as it’s performed under general anesthesia. The procedure usually takes one to two hours, and patients can return home on the same day. There are many benefits associated with this type of surgery, including improved physical appearance, increased self-confidence, and a better quality of life overall.
The major benefit of undergoing gynecomastia surgery is its ability to improve physical appearance significantly. Gynecomastia surgery will significantly improve the physical appearance of chest tissue. As a result, men who have undergone gynecomastia surgery often report feeling more confident about their bodies and less inhibited when wearing certain types of clothing or participating in activities that expose their chests, such as swimming or shirtless sports.
By improving physical appearance, gynecomastia surgery can ultimately increase overall psychological well-being by boosting confidence levels and improving body image perception. With these positive changes to mental and physical states, individuals may experience enhanced levels of happiness that positively affect other aspects of life, such as work performance or relationships with family members and friends.
Gynecomastia Surgery Conclusion
In conclusion, gynecomastia surgery can be a safe and beneficial option for those with abnormally large male breasts. Patients should seek experienced surgeons to ensure they receive the best care possible. Patients should feel comfortable having an honest conversation with their doctor about any potential discomfort or risks associated with the surgery to ease any anxiety before or after their procedure.
In most cases, gynecomastia surgery is a relatively straightforward process that yields positive results that far outweigh the brief period of pain felt during recovery. As the saying goes, “No pain, no gain”; sometimes, enduring discomfort now leads to greater peace of mind and improved self-confidence down the line! More questions like: Is Gynecomastia Painful? Ask this question and more during your consultation with us.
Read More

Dr.Babak Moeinolmolki
LA Cosmetic Surgeon Dr. Moein is board-certified by the American Board of General Surgery.

