Table of Contents
- Understanding Gynecomastia vs Chest Fat
- What is Gynecomastia?
- What is Chest Fat Men?
- Key Differences Between Gynecomastia and Chest Fat
- Methods to Differentiate Between Gynecomastia and Chest Fat
- Physical Assessment Techniques
- The Pinch Test Explained
- Gynecomastia vs Chest Fat: Evaluating Symptoms for a Diagnosis
- Treatment Options for Gynecomastia
- Gyno Surgical Procedures in Los Angeles: Liposuction vs. Gland Excision
- Non-Surgical Treatments Gyno LA
- Recovery and Expected Outcomes from Gyno Surgery
- Managing Chest Fat
- FAQs about Gynecomastia and Chest Fat
- Gynecomastia vs Fat: Get Expert Help in Los Angeles
Understanding Gynecomastia vs Chest Fat
How to Identify the Differences Gynecomastia and Chest Fat
Gynecomastia and chest fat are often misunderstood, yet they can significantly impact self-esteem and body image. Many individuals struggle to differentiate between these two prevalent conditions, leading to confusion and distress.
Gynecomastia, characterized by enlarged breast tissue in males, typically results from hormonal imbalances, while chest fat is more closely related to overall body fat levels. Understanding the differences in Gynecomastia vs chest fat is vital, as each condition requires a distinct approach for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment. Proper evaluation by a qualified specialist ensures that patients receive the most appropriate care, whether through lifestyle modification or surgical intervention.

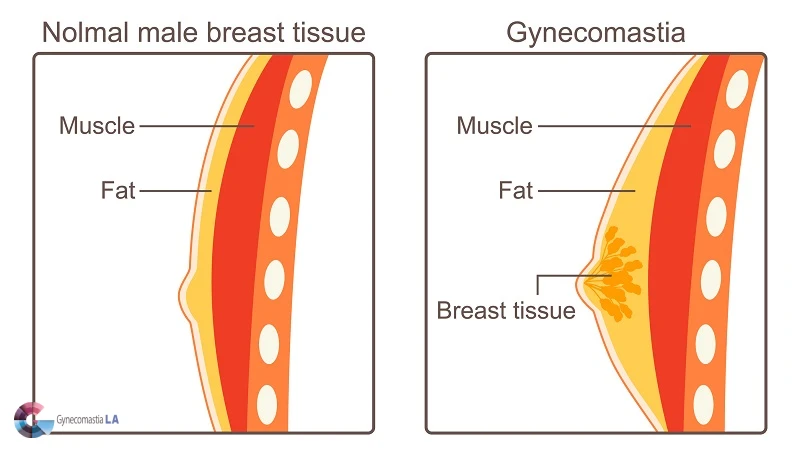
What is Gynecomastia?
Gynecomastia is a condition where men develop enlarged breast tissue. It often results from an imbalance between estrogen and testosterone levels in the body. This condition involves the presence of excess glandular breast tissue in males, which leads to a more feminine chest appearance. When evaluating Gynecomastia vs chest fat, it’s important to recognize that gynecomastia is caused by hormonal changes and involves firm glandular tissue, whereas chest fat is typically softer and related to excess body weight. Differentiating between the two is crucial for determining the most effective treatment approach.
🟨 Definition and Overview
Gynecomastia is the enlargement of glandular breast tissue in males. It differs from excess chest fat, which is known as pseudogynecomastia. True gynecomastia involves firm glandular tissue, whereas pseudogynecomastia is mostly fatty tissue. This condition can affect one or both breasts and may cause tenderness.
🟨 Common Causes of Gynecomastia
Gynecomastia can result from various factors, including:
- Hormonal Imbalances: A high level of estrogen compared to testosterone can cause enlarged breast tissue.
- Health Conditions: Liver diseases, kidney failure, and hormonal fluctuations are common culprits.
- Medications: Some drugs, like those for ulcers or certain antibiotics, can lead to gynecomastia.
- Lifestyle: Weight gain and a sedentary lifestyle can contribute by increasing adipose tissue.
- Substance Use: Alcohol and drugs like marijuana may also play a role.
Understanding these causes is essential for determining the appropriate gynecomastia treatment, which might include lifestyle changes or even surgical intervention for more severe cases.
What is Chest Fat Men?
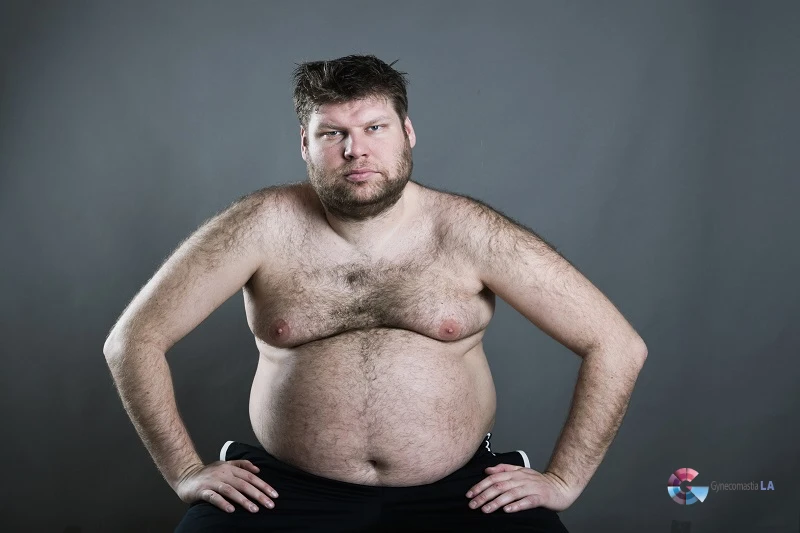

Chest fat, often known as “moobs,” is when excess fat collects in the chest area. This condition can affect males, causing them to have a more rounded chest appearance. It primarily involves fatty tissue, not glandular breast tissue. Many confuse it with gynecomastia, which involves excess breast tissue and is due to glandular issues.
🟨 Common Causes of Chest Fat
Several factors can lead to the build-up of chest fat in males:
- Weight Gain: Additional body fat often settles in the chest area.
- Sedentary Lifestyle: Lack of physical activity contributes to weight gain and fat accumulation.
- Unhealthy Diet: Consumption of high-calorie and high-fat foods can increase adipose tissue.
- Hormonal Imbalance: Changes in hormone levels, like reduced testosterone, may influence fat distribution.
- Health Conditions: Issues such as liver diseases or kidney failure can affect metabolism, leading to excess chest fat.
Understanding these causes can help identify whether the issue is due to lifestyle factors or a deeper medical condition.
Key Differences Between Gynecomastia and Chest Fat
Gynecomastia and chest fat may look similar, but they differ significantly. Gynecomastia involves excess breast tissue due to hormonal imbalance. This condition is common in males and causes enlarged glandular breast tissue. In contrast, chest fat is due to excess adipose tissue, often from weight gain or a sedentary lifestyle. Understanding these differences is important for correct diagnosis and treatment.
Hormonal Factors in Gynecomastia
Gynecomastia is often caused by fluctuating hormone levels. It’s the result of low testosterone levels and higher estrogen levels in males. Hormonal imbalances can arise due to several health conditions, including liver diseases and kidney failure. Understanding the hormone levels is crucial for identifying true gynecomastia, which may require gynecomastia treatment.
Physical Characteristics of Gynecomastia vs Chest Fat
Identifying whether your chest enlargement is gynecomastia or fat involves noting the physical characteristics. Gynecomastia is usually firm and centered around the nipple area with glandular tissue. On the other hand, chest fat feels softer and more spread out over the chest.
Symptoms: Tenderness and Discharge
Gynecomastia can cause tenderness or pain in the breast area. In some cases, there might be a discharge from the nipples. Chest fat, however, does not typically cause these symptoms. If tenderness or discharge is present, it may indicate a medical condition requiring assessment by a plastic surgeon or healthcare provider.
| Feature | Gynecomastia | Chest Fat |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Hormonal imbalance | Weight gain |
| Type of Tissue | Glandular breast tissue | Adipose (fatty) tissue |
| Location | Centered around nipples | Evenly spread on chest |
| Symptoms | Tenderness and possible discharge | Generally symptom-free |
For those experiencing these conditions, treatment options include adopting a healthy diet, increasing physical activity, and sometimes considering surgical intervention or breast reduction surgery if necessary. Always consult a medical professional to explore the best course of action.
Methods to Differentiate Between Gynecomastia and Chest Fat
Understanding the Root Cause Leads to the Right Solution
Gynecomastia and chest fat may appear similar, but they are fundamentally different conditions.
- Gynecomastia involves excess glandular breast tissue caused by hormonal imbalance.
- Chest fat is simply the accumulation of adipose tissue, often due to weight gain or inactivity.
Understanding the differences in Gynecomastia vs chest fat is essential for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Physical Assessment Techniques
How Professionals Identify the Underlying Condition
Physicians use clinical palpation techniques to evaluate the chest area:
- Glandular tissue (as seen in gynecomastia) is firmer and more nodular.
- Fatty tissue (as in chest fat) is soft and spread across the chest.
These manual exams help identify whether the enlargement is due to true gynecomastia or fat accumulation.
The Pinch Test Explained
A Simple Diagnostic Tool
The pinch test is often used to distinguish tissue types:
- Soft, pliable, thick skin fold = likely chest fat.
- Firm, disc-like mass beneath the nipple = likely gynecomastia.
This non-invasive method offers quick insights during clinical evaluation.
Gynecomastia vs Chest Fat: Evaluating Symptoms for a Diagnosis
Recognizing When Further Medical Attention is Needed
Look for the following symptoms:
- Tenderness or pain in the breast area.
- Nipple discharge (rare but concerning).
- Unilateral or asymmetrical breast development.
These symptoms often point to hormonal imbalance or an underlying medical condition, such as:
- Liver dysfunction
- Kidney failure
- Endocrine disorders
Gynecomastia may require medical or surgical treatment.
Chest fat typically improves with diet, exercise, and weight loss.
Treatment Options for Gynecomastia
Effective Solutions Based on Severity and Root Cause
Gynecomastia is the enlargement of breast tissue in males, typically resulting from a hormonal imbalance such as lower testosterone levels or increased estrogen. This excess tissue may appear similar to fat, but it often stems from glandular breast tissue rather than adipose (fat) tissue. Understanding the difference between gynecomastia vs chest fat is important, as true gynecomastia involves firm, rubbery tissue beneath the nipple that may not respond to diet or exercise, whereas fat accumulation is usually softer and more diffuse. The duration of gynecomastia can vary depending on its cause. In adolescents, it is often temporary and may resolve on its own within six months to two years as hormone levels stabilize.
Gyno Surgical Procedures in Los Angeles: Liposuction vs. Gland Excision
Surgical treatment is one of the most effective solutions, especially in moderate to severe cases. The technique selected depends on the composition of the chest tissue.
🔵 Liposuction
- ✅ Purpose: Removes excess fatty tissue from the chest.
- 🧍♂️ Best For: Patients with pseudo-gynecomastia or soft, fat-based enlargement.
- 💡 Benefit: Minimally invasive with a shorter recovery time.
🟢 Gland Excision
- ✅ Purpose: Removes glandular breast tissue located beneath the nipple.
- 🧑⚕️ Best For: Men with true gynecomastia involving firm glandular growth.
- 💡 Benefit: More defined chest contour; resolves the root cause of tissue enlargement.
💬 Both procedures, liposuction and gland excision, can be combined when both fatty and glandular tissues are present. Your plastic surgeon will recommend the best approach based on an individual exam and imaging.
Non-Surgical Treatments Gyno LA
For those in the early stages or with mild symptoms, non-surgical options may offer relief, especially when addressing underlying hormonal causes.
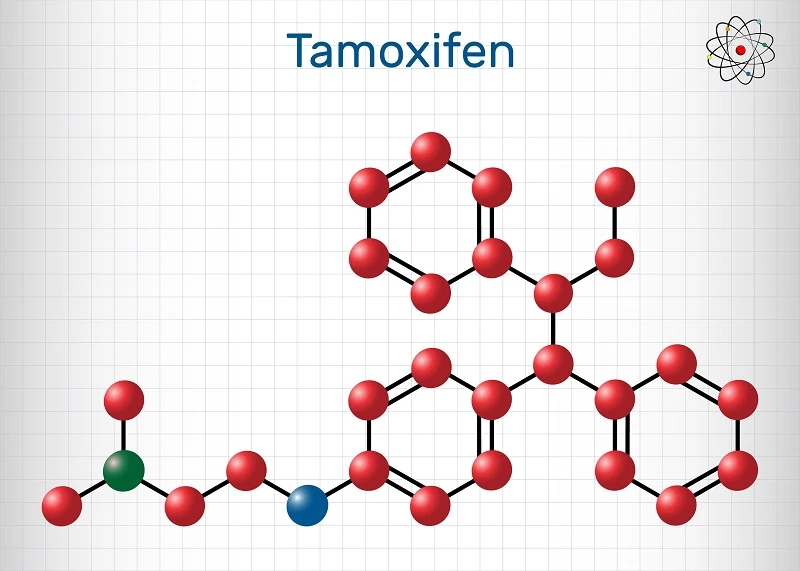
🟠 Medications
- 💊 Drugs like Tamoxifen or aromatase inhibitors may help balance estrogen and testosterone.
- 🔄 Used in cases where gynecomastia is linked to medication use or hormonal disorders.
🟣 Healthy Diet & Exercise
- 🥗 Focus on whole foods, reduced sugars, and lean proteins.
- 🏋️ Incorporate cardio and resistance training to burn fat and boost testosterone.
- 📉 May improve male chest appearance in pseudo-gynecomastia but less effective for glandular tissue.
⚠️ These methods are not substitutes for surgery when true gynecomastia is present, but they are vital for long-term health and maintenance.
Recovery and Expected Outcomes from Gyno Surgery
🔵 Post-Surgery Care
- 🩹 Swelling and bruising are expected and usually subside within 1–2 weeks.
- 🧥 Compression garments are worn to minimize swelling and assist healing.
🟢 Physical Activity
- 🚫 Restricted for the first 2–3 weeks post-op.
- 🏃♂️ Gradual return to full activity typically allowed after 4–6 weeks.
🟣 Surgical Outcomes
- ✅ High satisfaction rates.
- 💪 Noticeable improvement in male chest definition and masculine contour.
- 📷 Ideal for patients looking for lasting, aesthetic improvement.
Long-Term Consideration: If the underlying cause (e.g., liver disease, medication use, or hormonal fluctuation) is not corrected, recurrence may occur. Ongoing medical management may be necessary.
Managing Chest Fat
Managing chest fat begins with understanding the difference between fat and gynecomastia. True gynecomastia involves glandular breast tissue growth in males due to hormonal imbalance. Chest fat, on the other hand, is usually a result of excess fatty tissue from weight gain or a sedentary lifestyle. Knowing these differences is vital for choosing the right treatment option.
Lifestyle Changes: Diet and Exercise
A healthy diet and regular exercise are key to managing chest fat. Start by reducing your intake of processed foods and sugars. Focus on a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains. Incorporate cardiovascular and strength training exercises to reduce excess chest fat and improve body composition. A consistent exercise routine can adjust hormone levels, helping decrease fatty tissue and boost testosterone levels.
Weight Loss Impact on Chest Fat
When you lose weight, you’ll likely notice a reduction in excess chest fat. Weight loss helps decrease adipose tissue, leading to a more toned appearance. It’s important to note that weight loss alone may not resolve all issues if there is glandular breast tissue present. However, for many, shedding excess pounds can significantly reduce their chest size and improve overall health conditions.
Long-term Maintenance Strategies
To maintain results and prevent the return of excess chest fat, adopt long-term strategies. Continue a balanced and nutrient-rich diet to support hormonal health. Maintain a regular exercise schedule to keep sedentary habits at bay. Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider can help monitor hormone levels and detect any medical conditions early. If lifestyle changes aren’t enough, consult a cosmetic surgeon for potential surgical options, like gynecomastia surgery, to remove excess tissue.
FAQs about Gynecomastia and Chest Fat
Understanding the differences between gynecomastia and chest fat is important. Gynecomastia involves excess breast tissue due to a hormonal imbalance. This results in glandular breast tissue in males. In contrast, excess chest fat is usually the result of weight gain and is comprised of fatty tissue. Below are some frequently asked questions that help clarify these conditions.
Can Gynecomastia Resolve on Its Own?
Yes, gynecomastia can resolve on its own, especially during puberty. Hormonal fluctuations often cause gyno in teenage boys, and as hormone levels stabilize, the condition may improve. However, in adults, true gynecomastia might persist unless treated. It’s important to consult with a healthcare provider to explore gynecomastia treatment options.
What Role Does Weight Loss Play in Both Conditions?
Weight loss can significantly impact excess chest fat, which is caused by adipose tissue from weight gain. A healthy diet and regular exercise can reduce this excess fat. However, weight loss alone may not fully resolve gynecomastia. This condition is more related to glandular tissue than fat, requiring a possible medical or surgical intervention.
| Condition | Role of Weight Loss |
|---|---|
| Chest Fat | Often helps reduce excess chest fat |
| Gynecomastia | Limited effect since it’s glandular tissue |
Gynecomastia vs Fat: Get Expert Help in Los Angeles
Distinguishing between gynecomastia vs fat is essential for determining the most effective treatment approach. While excess chest fat can often be managed through lifestyle changes, true gynecomastia involving glandular breast tissue typically requires specialized care. At the Gynecomastia LA Center, we offer comprehensive Men Gyno Services tailored to each patient’s unique needs. Whether you’re experiencing persistent gynecomastia, have had unsatisfactory results from prior procedures, or are considering revision gynecomastia surgery, board-certified gynecomastia surgeon Dr. Moein provides advanced surgical solutions in Los Angeles and Beverly Hills.
If you’re ready to take the next step, we encourage you to explore our articles to learn more about your options, or reach out through our contact form to schedule a private consultation. For immediate assistance, call us today at 310-861-3799. Your journey to a more confident you begins here with trusted care from one of the leading specialists in male chest contouring.

Dr.Babak Moeinolmolki
LA Cosmetic Surgeon Dr. Moein is board-certified by the American Board of General Surgery.

