Table of Contents
- Understanding Will Increasing Testosterone Reduce Gynecomastia?
- Overview Gynecomastia
- The Role of Testosterone in the Male Body
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT)
- Evaluating Testosterone as a Solution for Gynecomastia
- Non-Surgical and Surgical Solutions for Treating Gynecomastia
- Final Thoughts: Will Increasing Testosterone Reduce Gynecomastia?
Understanding Will Increasing Testosterone Reduce Gynecomastia?
Gynecomastia, the enlargement of breast tissue in males, often sparks both curiosity and concern due to its prevalence and psychological impact. This
common condition can result from a myriad of factors, including hormonal imbalances and lifestyle influences. Understanding its root causes and manifestations is crucial for those seeking effective remedies.
In the male body, testosterone plays a pivotal role, governing various physiological processes and physical characteristics. Yet, when testosterone levels fall or become imbalanced with other hormones like estrogen, unusual changes such as gynecomastia can emerge. This imbalance prompts many men to wonder: will increasing testosterone reduce gynecomastia? Thus, the potential of testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) as a corrective measure brings both promise and caution due to possible ramifications.

This article explores the complex relationship between testosterone and gynecomastia, delving into whether increasing testosterone levels could offer relief. It investigates therapeutic interventions, the risks involved, and alternative treatments, advocating for informed, personalized medical evaluations to guide appropriate strategies for those affected.
Overview Gynecomastia
Gynecomastia is a condition that affects many men around the world, leading to concerns about the growth of breast tissue. This issue can cause physical and emotional discomfort, as men may feel self-conscious about their appearance. To understand gynecomastia, it’s important to explore its causes, symptoms, and treatment options. Being informed about these factors can help individuals make educated choices about their health and seek appropriate medical care. Let’s take a closer look at what gynecomastia is, why it occurs, and how it can be diagnosed.
Definition of Gynecomastia
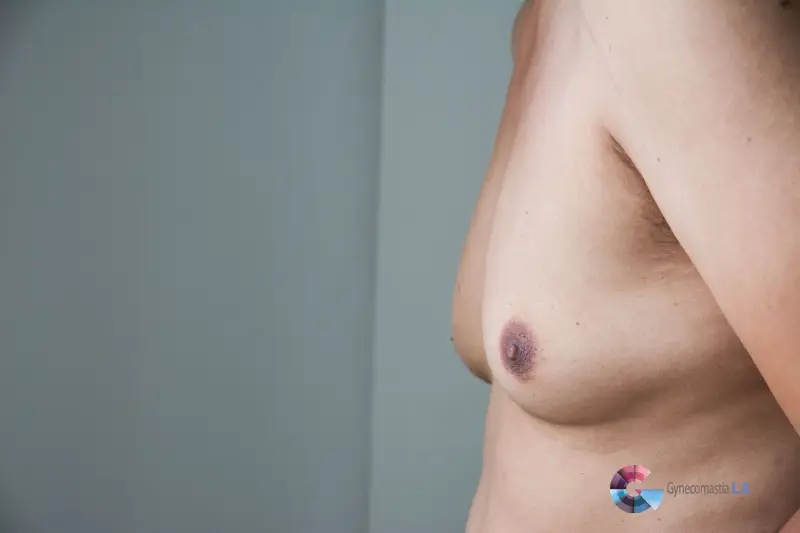
Gynecomastia is defined as the enlargement of breast tissue in males, which can occur due to various reasons. It is important to note that gynecomastia is different from having excess fat tissue in the chest. While it might look similar to chest fat, gynecomastia involves the growth of glandular breast tissue. This condition can appear at different life stages, including puberty, adulthood, or as a result of aging. Often, gynecomastia is linked to hormonal imbalances, where testosterone levels are lower compared to estrogen levels. While gynecomastia might seem permanent, in many cases, it can be treated through lifestyle changes, medications, or surgical intervention.
Common Causes of Gyno
Gynecomastia can be caused by several factors, primarily involving hormonal changes. It is often linked to an imbalance between testosterone and estrogen levels in the body. Here are some common causes:
- Hormonal Imbalances: Decreased testosterone and increased estrogen production can lead to the development of excess breast tissue.
- Health Conditions: Conditions such as liver disease, kidney failure, or thyroid problems can contribute to the risk of gynecomastia.
- Medications and Substances: Certain drugs, including steroids, anti-anxiety medications, and some antibiotics, may cause gynecomastia as a side effect. Alcohol and drugs like marijuana can also impact hormone levels.
By knowing the potential causes, individuals can consult with healthcare providers to determine if any underlying health issues or substances might be contributing to their condition.
Symptoms and Diagnosis of Gyno
The symptoms of gynecomastia include swelling and tenderness in the breast tissue. Some individuals may also notice asymmetric breast development or feel self-conscious about the appearance of their chest. Diagnosing gynecomastia often involves a physical examination by a doctor. They will assess the size of the breast tissue and check for any potentially concerning lumps. This helps identify the type and severity of gynecomastia, guiding treatment decisions and ruling out serious conditions.
In addition to the physical exam, a doctor might recommend blood tests to evaluate hormone levels, helping to identify any underlying hormonal imbalances. Imaging tests, such as mammograms or ultrasounds, may also be conducted to ensure there are no other health concerns like breast cancer. It’s essential for those experiencing symptoms to seek a professional diagnosis to determine the best course of treatment and rule out other conditions.
The Role of Testosterone in the Male Body
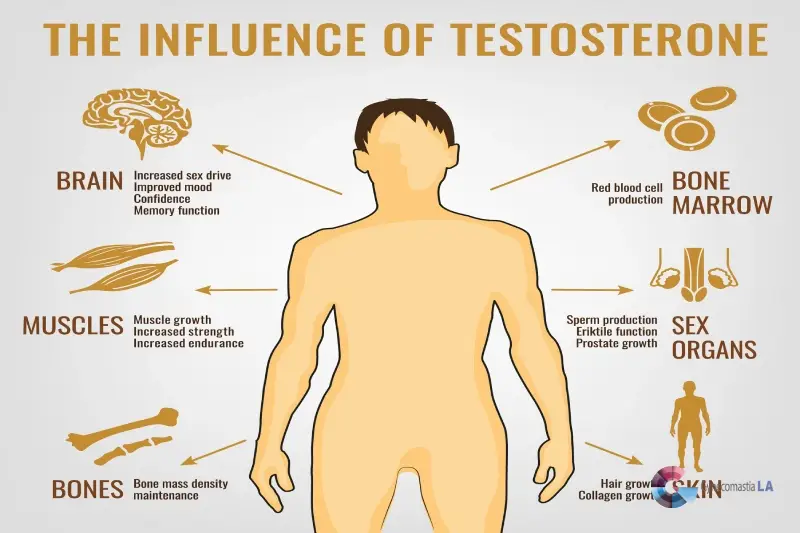
Testosterone is a key hormone that plays a vital part in the male body. It affects many functions, from physical traits to mental well-being. It is often linked with muscle growth, energy levels, and mood. But its role is even broader. Testosterone helps with fat distribution and maintaining a healthy sex drive too. It even plays a part in the production of red blood cells. Understanding the role of testosterone is crucial for addressing various health issues. This hormone is integral to a man’s overall health and well-being.
Functions of Testosterone
Testosterone supports various functions that are essential for health and development. It aids in muscle growth and repair. This is why athletes and bodybuilders often focus on their testosterone levels. Additionally, testosterone influences bone density, helping to keep bones strong. It also has a role in fat distribution, affecting how fat is stored and used in the body. Beyond physical attributes, testosterone impacts mental health too. Adequate levels can help improve mood and mental clarity. This hormone is also vital for sexual health, affecting libido and fertility. Thus, testosterone is key to both physical and emotional aspects of a man’s life.
Hormonal Imbalance and Gynecomastia
Hormonal imbalances can be triggered by various factors. Some of these include natural changes in hormone production during puberty or aging. Health conditions like kidney failure, liver disease, and tumors can also disrupt hormone levels. Additionally, certain medications and drugs can affect how hormones are produced and regulated. This hormonal shift can lead to increased estrogen levels or decreased testosterone, both of which contribute to the development of gynecomastia. Recognizing these causes can help in identifying and addressing gynecomastia early.
Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT)
Testosterone Replacement Therapy is a medical treatment for men with low testosterone levels, a condition known as hypogonadism. Low testosterone can lead to fatigue, low sex drive, and muscle loss. TRT can improve these symptoms, but it is essential to discuss the benefits and risks with a doctor. Regular monitoring of hormone levels is crucial for safe treatment.
TRT is administered through injections, patches, gels, or implants and aims to restore testosterone to normal levels, enhancing energy, mood, and muscle strength. However, not everyone is a candidate, and side effects like sleep apnea, skin reactions, and increased blood cell counts may occur.
TRT and Gynecomastia

Gynecomastia, or breast tissue enlargement in males, can occur due to hormonal imbalances, including increased estrogen. While TRT can balance hormones, excess testosterone may convert to estrogen, potentially worsening gynecomastia. Monitoring estrogen levels is important, and consulting a specialist may be necessary for effective treatment.
Risks and Side Effects of TRT
While TRT can alleviate symptoms like reduced sex drive or fatigue, it also carries risks. Side effects may include mood changes, increased anger, acne, or increased red blood cell count, which can raise the risk of blood clots. Monitoring cholesterol levels is important to prevent heart disease.
The long-term effects of TRT are still being researched, with concerns about potential links to heart disease and prostate health issues. Regular check-ups are vital to manage any adverse conditions that may arise from extended use of testosterone therapy.
Evaluating Testosterone as a Solution for Gynecomastia
Gynecomastia, characterized by enlarged male breast tissue, is often linked to hormonal imbalances, particularly high estrogen and low testosterone levels. Some individuals consider increasing testosterone to reduce or eliminate this condition through testosterone replacement therapy (TRT). However, the effectiveness of this approach can vary.
Case Studies and Research Findings
Research presents mixed results regarding testosterone’s impact on gynecomastia. While some studies suggest that boosting testosterone may help reduce breast tissue by counteracting excess estrogen, not all patients experience significant improvements. Factors such as age, health, and the underlying cause of gynecomastia play critical roles in treatment outcomes. Testosterone therapies may be more effective when gynecomastia is due to low hormone levels, yet they may not suffice if other issues, like medications or persistent hormonal imbalances, are at play.
Is Increasing Testosterone Always Effective?
Increasing testosterone does not guarantee results for everyone. Persistent symptoms may indicate that other issues, like high estrogen levels, are more significant. Additionally, TRT comes with potential side effects, including mood changes and risks to natural hormone production. Individuals should consult healthcare professionals to understand the benefits and risks of treatment.
While increasing testosterone may help some men, effective treatment requires thorough diagnosis and individualized care.
Non-Surgical and Surgical Solutions for Treating Gynecomastia
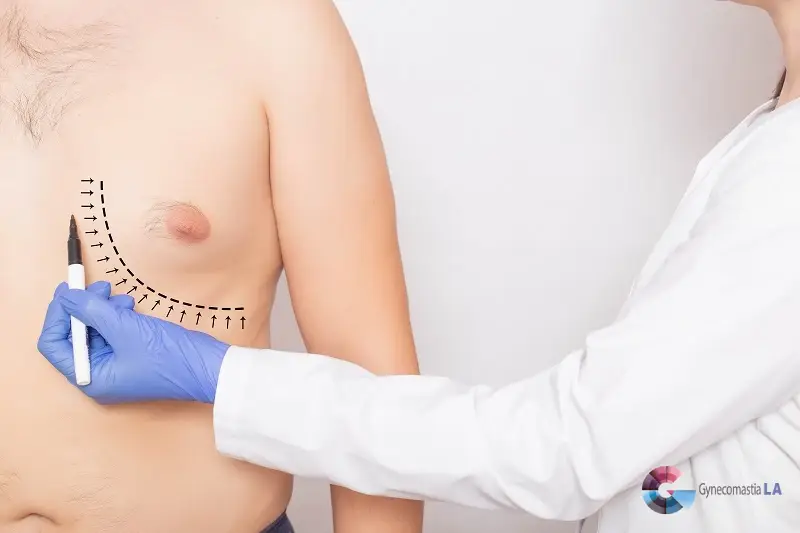
For those seeking non-surgical options, certain medications like selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs) and aromatase inhibitors can help address hormonal imbalances. Lifestyle changes, including weight loss and exercise, may also improve symptoms. If these methods are ineffective, surgical options such as breast reduction surgery can provide a more permanent solution, with skilled surgeons aiming to minimize scarring during recovery.
Medications and Non-TRT Options
For men with gynecomastia seeking non-surgical treatments, medications can be effective. Hormonal adjustments can be made with selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs) like tamoxifen, which blocks estrogen, and aromatase inhibitors that lower estrogen production. Lifestyle changes, such as weight loss and exercise, can also help. Consulting healthcare professionals is essential for a tailored treatment plan to minimize side effects.
Surgical Solutions for Gynecomastia
If medications and lifestyle changes do not provide satisfactory results, surgical options like breast reduction surgery may be considered. This procedure removes excess breast tissue and fat to achieve a flatter chest. While some scarring may occur, skilled surgeons strive to minimize it. Recovery typically involves some downtime, and proper care can lead to positive outcomes.
Final Thoughts: Will Increasing Testosterone Reduce Gynecomastia?
Determining whether an increase in testosterone levels can alleviate gynecomastia requires a deep understanding of the unique hormonal landscapes that vary from patient to patient. For some individuals, elevating testosterone through carefully monitored replacement therapy may provide much-needed relief. However, others might find that alternative routes—such as targeted medications, lifestyle modifications, or even surgical options—are necessary for effective treatment.
Dr. Moein, a distinguished gynecomastia surgeon, excels in crafting attentive and personalized assessments tailored to each individual’s needs. Practicing at the forefront of his field in the bustling locales of Los Angeles and Beverly Hills, he offers expert gynecomastia surgery, ensuring that each patient receives compassionate care and a detailed explanation of their treatment options.
Moreover, Dr. Moein is dedicated to making the journey to regaining confidence as seamless as possible, providing clarity on insurance coverage and offering flexible financing solutions for his patients. If you’re ready to explore the possibilities and take a bold step towards reclaiming your confidence, don’t hesitate to schedule your appointment today using our easily accessible contact form.

Dr.Babak Moeinolmolki
LA Cosmetic Surgeon Dr. Moein is board-certified by the American Board of General Surgery.

