Table of Contents
Introduction: Male Chest Types
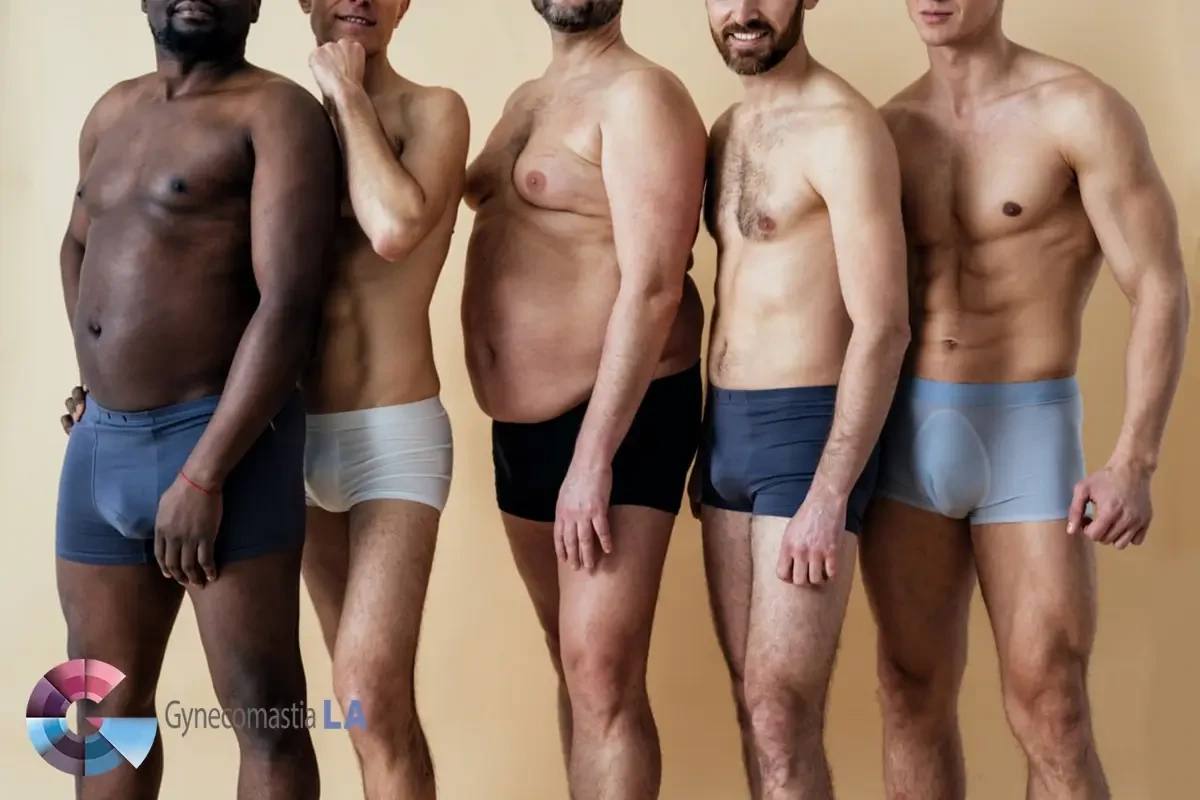
The male chest can vary greatly in appearance, with different types characterized by their unique features. One condition that can affect the male chest is gynecomastia, which is the development of excessive breast tissue. This condition can be caused by hormonal imbalances, medications, certain medical conditions, or lifestyle factors such as obesity or drug use.
Aside from gynecomastia, the male chest can also undergo variations in appearance due to aging, excess body weight, poor skin quality, and unfavorable anatomy. As men age, their chest can become saggy or develop loose skin. Excess body weight can lead to a larger, less defined chest, while poor skin quality can result in wrinkles or stretch marks. Unfavorable anatomy, such as pectus excavatum or pectus carinatum, can also affect the appearance of the male chest.
The concept of an “ideal” male chest is often associated with defined contours, a natural fold just below the chest, and specific measurements for nipple placement and areola protrusion. The presence of well-defined pectoral muscles is highly desirable, creating a more masculine and chiseled appearance. Nipple placement can significantly impact the overall aesthetics of the chest, with specific measurements and proportions considered to achieve an ideal result.
In conclusion, understanding the different types of male chest, including gynecomastia and its causes, as well as the variations in chest appearance due to aging, excess body weight, poor skin quality, and unfavorable anatomy, is essential in the pursuit of an ideal male chest. By considering these factors, individuals can work towards achieving their desired chest appearance and enhance their self-confidence.
Ideal Male Chest
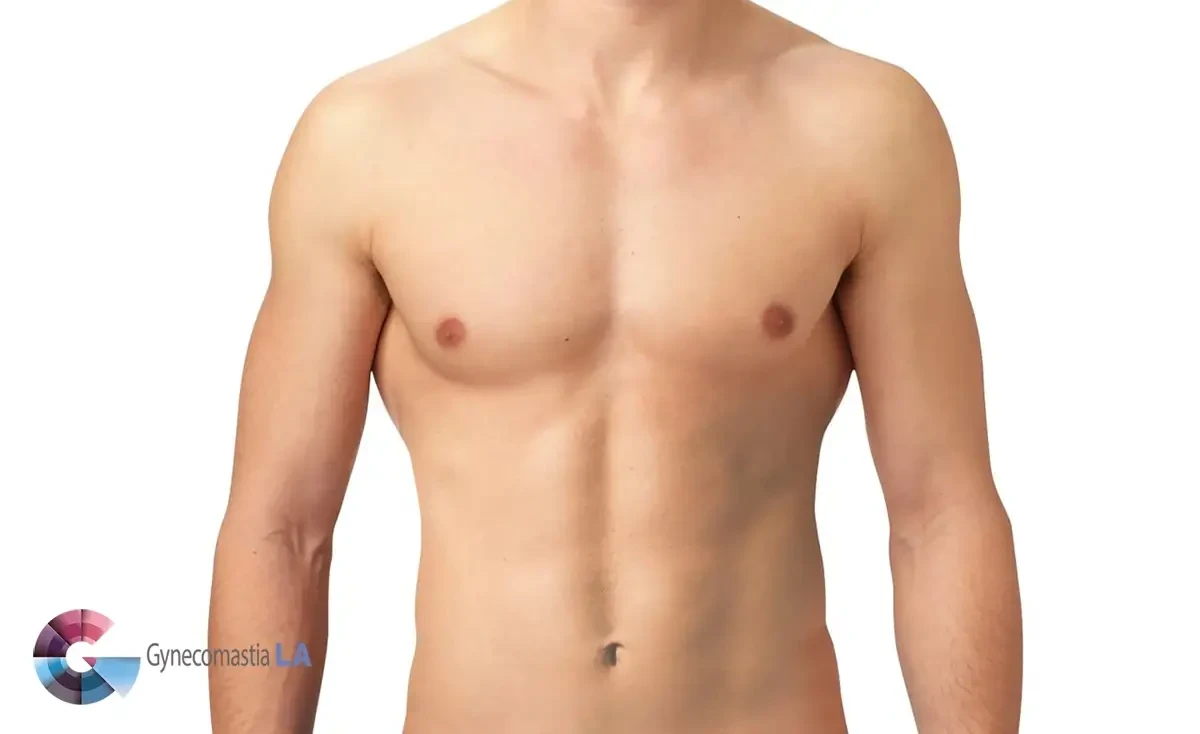
The ideal male chest is often characterized by a well-defined contour and a balanced aesthetic appearance. The contour of the chest should be smooth and proportionate, with a gradual slope from the clavicle to the lower ribcage. It should exhibit a masculine appearance, emphasizing muscle definition rather than excessive bulk.
The nipple position in the ideal male chest is usually parallel to the midclavicular line, which is an imaginary vertical line running through the center of the collarbone. The nipples should be positioned slightly higher on the chest, usually at the level of the fourth or fifth rib. This placement contributes to a more youthful and attractive appearance, while avoiding a saggy or drooping look.
Areola appearance is another important consideration. In the ideal male chest, the areolas are generally small to medium in size and have a circular or slightly oval shape. They should be darker in color, ranging from light to medium brown, with a smooth texture and minimal variation in pigmentation.
In terms of fat presence, the ideal male chest typically has minimal fat accumulation. It should be toned and firm, with well-defined musculature. While some individuals may naturally have a small amount of fat overlying the pectoralis major muscle, excessive fat can obstruct muscle visibility and create an undesired roundness.
The pectoralis major muscle plays a critical role in defining the ideal male chest. It should appear well-developed and symmetrical, with a defined upper and lower border. The chest fold, where the pectoralis major muscle meets the ribs, should be well-defined but not excessively deep or marked. A smooth transition between the muscle and the chest fold contributes to an appealing and fit appearance.
In conclusion, the ideal male chest exhibits a smooth contour, with nipples positioned parallel to the midclavicular line and areolas that are small to medium with a uniform pigmentation. It should have minimal fat presence, allowing for well-defined musculature, particularly the pectoralis major muscle. The chest fold should be well-defined but not overly pronounced. Striving for these characteristics can help individuals achieve a more desired masculine aesthetic for their chest.

Undesirable Male Chest
The male chest is often seen as a symbol of strength and masculinity. However, there are instances where men may feel self-conscious or uncomfortable with certain aspects of their chest, leading to the development of an undesirable male chest. This can refer to conditions such as gynecomastia, excess fat deposits, or sagging skin that may disrupt the individual’s desired physique. In this article, we will explore the reasons behind an undesirable male chest and discuss possible solutions to help men regain confidence in their appearance.
Fatty Chest
A fatty chest, also known as gynecomastia, is a condition characterized by the excess accumulation of fat in the chest area of males. It differs from chest fat, which refers to the normal distribution of fat in both males and females.
There are several causes and factors that contribute to the development of a fatty chest. Hormonal imbalances, such as an increase in estrogen levels or a decrease in testosterone levels, can lead to the enlargement of the mammary glands and subsequent fat deposition in the chest. Certain medications, such as anabolic steroids or anti-androgens, can also be a contributing factor. Additionally, obesity, excessive alcohol consumption, and certain medical conditions like hypogonadism or liver disease can increase the risk of developing a fatty chest.
While a fatty chest is generally a benign condition, it can havke several health implications and concerns. It can lead to psychological distress, self-esteem issues, and body image concerns due to the feminization of the male chest. It may cause physical discomfort, such as tenderness or pain. In some cases, it may also indicate an underlying health condition that requires further investigation.
In conclusion, a fatty chest, or gynecomastia, is characterized by the excess accumulation of fat in the male chest. Various causes and factors can contribute to its development. While it is generally harmless, it can have significant health implications and concerns. Seeking medical advice is recommended to address any physical or psychological issues associated with a fatty chest.
Glandular Chest
Glandular chest, commonly known as “man boobs,” refers to the development of glandular tissue under the nipples in men. It is a condition characterized by the enlargement of the breast tissue, leading to a feminine appearance in the chest area.
This condition is typically caused by hormonal imbalances, specifically an excess of estrogen or a decrease in testosterone levels. Glandular chest can also be a side effect of certain medications, such as anti-depressants, anabolic steroids, and medications used to treat prostate cancer.
Treating glandular chest involves addressing the underlying cause. If hormonal imbalances are the main issue, hormone replacement therapy may be recommended to restore the balance of hormones in the body. In some cases, surgery may be an option to remove the excess glandular tissue and reshape the chest.
In addition to medical interventions, lifestyle changes can also play a role in the management of glandular chest. Regular exercise, especially exercises targeting the chest muscles, can help to reduce the appearance of glandular chest. A healthy diet that is low in processed foods and high in fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins may also contribute to overall weight loss and reduction of excess breast tissue.
In conclusion, glandular chest is a condition characterized by the development of glandular tissue under the nipples in men. It is often caused by hormonal imbalances and certain medications. Treatment options include medication, surgery, and lifestyle changes, all aimed at reducing the appearance of glandular chest.
Saggy Skin Chest
Saggy skin chest, also known as ptosis of the breast, can be caused by various factors such as significant weight loss or aging. When a person loses a considerable amount of weight, the skin on their chest area may fail to shrink at the same rate, resulting in excess, loose skin. Additionally, as we age, the collagen and elastin fibers in our skin start to break down, leading to a loss of elasticity and sagging.
Several treatment options are available for saggy skin chest depending on the severity and individual preferences. Surgical methods include breast lift or mastopexy, which involves removing excess skin and reshaping the breast tissue to achieve a more lifted and firm appearance. This procedure may be combined with breast augmentation or reduction if desired.
Non-surgical methods for tightening and improving the appearance of saggy skin chest include exercises targeting the pectoral muscles and the use of topical creams or lotions containing ingredients like retinol or collagen. These products can help improve skin elasticity and promote collagen synthesis.
Other non-invasive options include laser treatments, radiofrequency therapy, or ultrasound therapy. These treatments stimulate collagen production and tighten the skin without surgery.
In conclusion, saggy skin chest can be a result of significant weight loss or aging, causing a loss of skin elasticity. Treatment options range from surgical procedures like breast lift to non-surgical alternatives such as exercises, topical creams, or various cosmetic procedures. Seeking medical advice from a qualified professional can help determine the most suitable treatment option for each individual.
Conclusion: Male Chest Types
In conclusion, understanding the different types of male chest in relation to gynecomastia is crucial for diagnosis and treatment. There are primarily two key types: glandular and adipose.
The glandular type is characterized by excessive breast tissue growth due to hormonal imbalances and is commonly associated with puberty or certain medical conditions. This type of chest typically has firm, rubbery tissue beneath the nipple area. In contrast, adipose type gynecomastia is caused by excess fat deposition in the chest area and is often linked to obesity or weight gain. It has a soft, pliable texture.
Both types of gynecomastia differ from the ideal male chest, which generally has a flat and muscular appearance. The ideal chest is defined by well-developed pectoral muscles and limited breast tissue, resulting in a masculine and athletic physique.
Recognizing the characteristics and features of each male chest type is essential for accurate assessment and appropriate treatment. Glandular gynecomastia requires hormonal regulation or surgical intervention to remove the excess breast tissue. Adipose gynecomastia can be managed through lifestyle modifications, such as healthy diet and regular exercise, to reduce overall body fat.
In summary, familiarizing oneself with the various types of male chest in relation to gynecomastia is crucial. Glandular and adipose gynecomastia each have distinct characteristics and differ from the ideal male chest. Accurate identification is vital for implementing the most suitable treatment approach and achieving desired outcomes.

Dr.Babak Moeinolmolki
LA Cosmetic Surgeon Dr. Moein is board-certified by the American Board of General Surgery.

